Resolving a multi-step atomic layer deposition surface reaction
Scientific Achievement
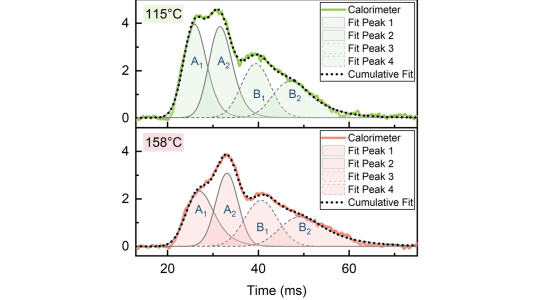
We utilized time-resolved microcalorimetry to reveal that the atomic layer deposition (ALD) of ZrO2 proceeds through at least two distinct surface reactions separated in time. A new mechanism is required to explain the observed reaction heat from sequential surface reactions that also depend on growth temperature.
Significance and Impact
A deeper understanding of surface reactions is required to better design and fabricate the interfaces on which microelectronics, catalysis, and energy conversion depend. In situ ALD calorimetry provides the most detailed thermodynamic and kinetic insights to date.
Research Details
- Calibrated microcalorimetry quantified the reaction heat of ZrO2 ALD, which matches the standard heat of formation
- ZrO2-forming surface reactions were investigated computa- tionally and found to incompletely describe reaction heat
Argonne National Laboratory seeks solutions to pressing national problems in science and technology by conducting leading-edge basic and applied research in virtually every scientific discipline. Argonne is managed by UChicago Argonne, LLC for the U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science.
The U.S. Department of Energy’s Office of Science is the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States and is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, visit https://energy.gov/science.