Engineering / Manufacturing and Smart Energy
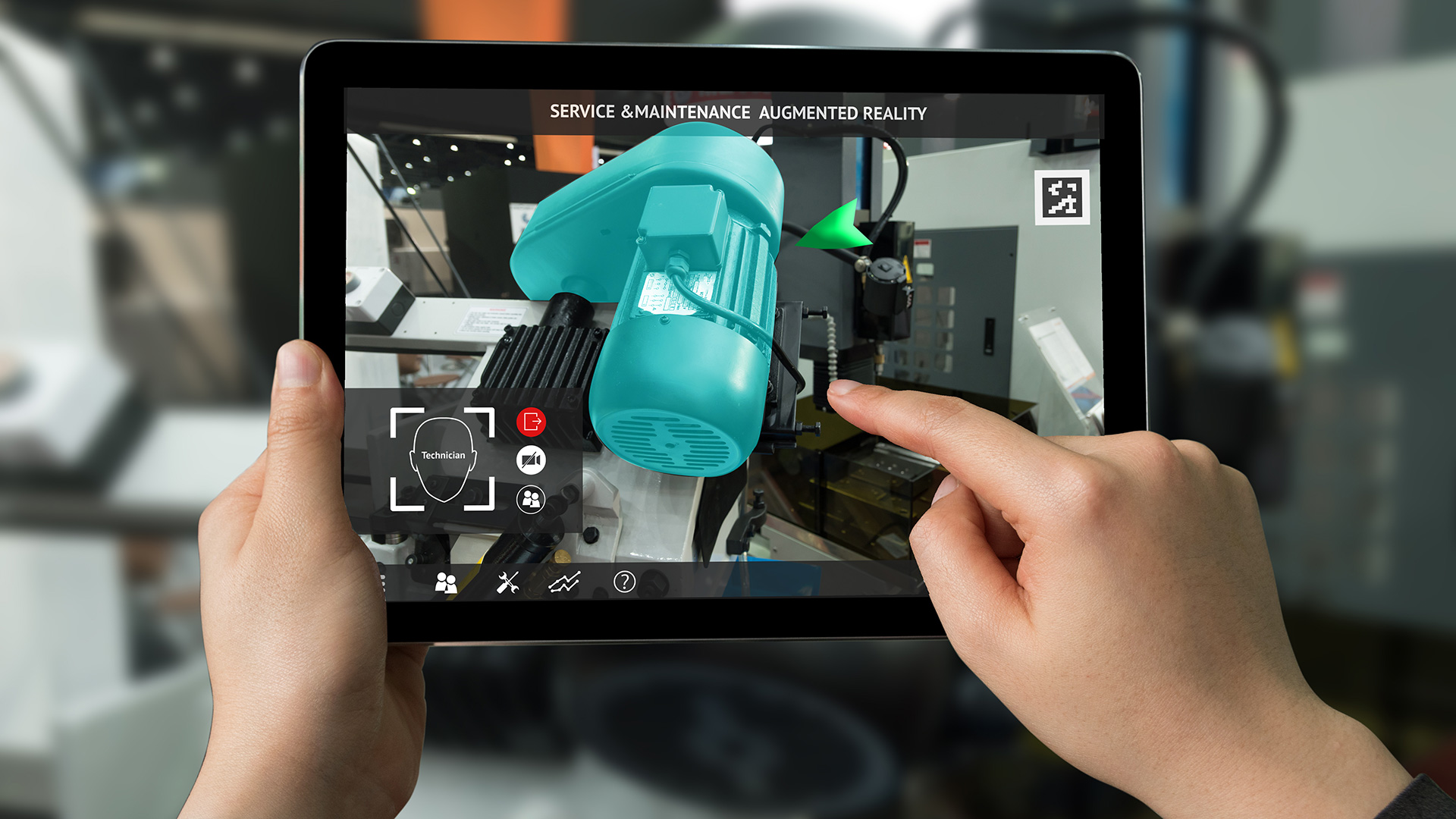
AIThe future of manufacturing hinges on the ability to bring new ideas and custom products to market faster than ever before while reducing cost, energy use, and waste products. Over the last decade, advances in technologies such as sensors, networks, and control systems — along with the rise of data analytics and AI approaches such as machine learning — have led to increasingly holistic approaches to manufacturing and engineering. Researchers have proposed transformational approaches, including optimization of the entire manufacturing lifespan —from raw materials to shape/topology to manufacturing process to end use. Machine learning and pattern recognition software can be used in manufacturing to inspect and assemble parts, identify flaws, reduce product development cycles, reduce waste, predict system failures, and more.
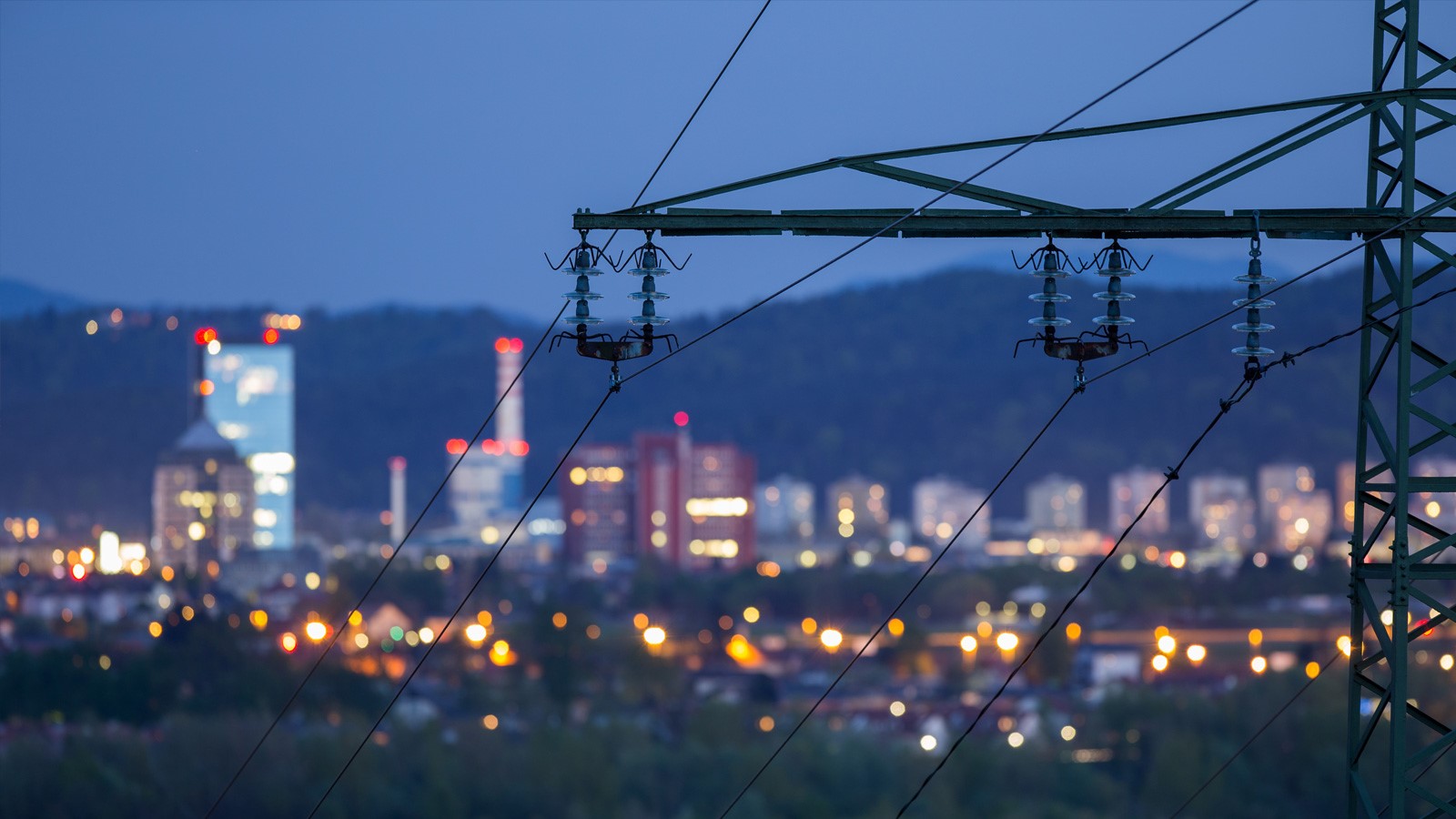
A number of factors are posing a significant challenges to coordinated operation of the nation’s power grid: intermittent renewable energy sources, increasing use of electric vehicles, deployment of decentralized power generation/storage facilities, and the impacts of long-term climate change and short-term extreme weather on energy infrastructure, among others. Urban planners have an increasing need for better tools to improve their infrastructure and prepare for future demands. AI tools will help enable a smart energy infrastructure that meets energy demands at multi-spatial and temporal scales and operates intelligently to achieve energy efficiency, flexibility, and resilience.